For equal fuel heat, the 4 stroke engine cycle converts more heat to work than the Carnot cycle.
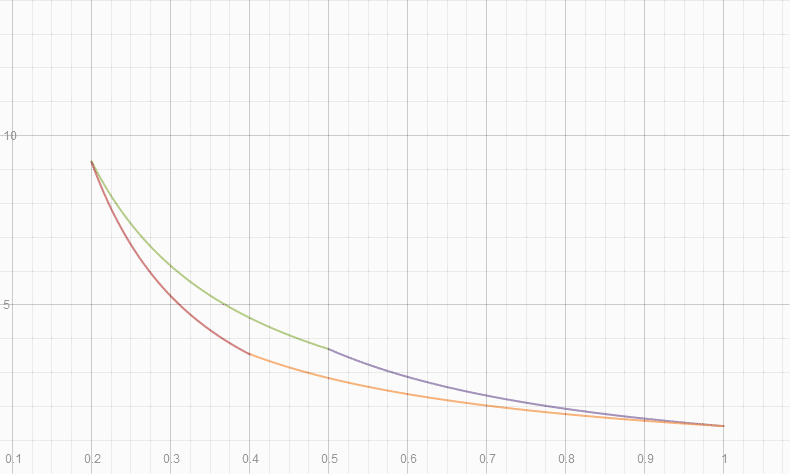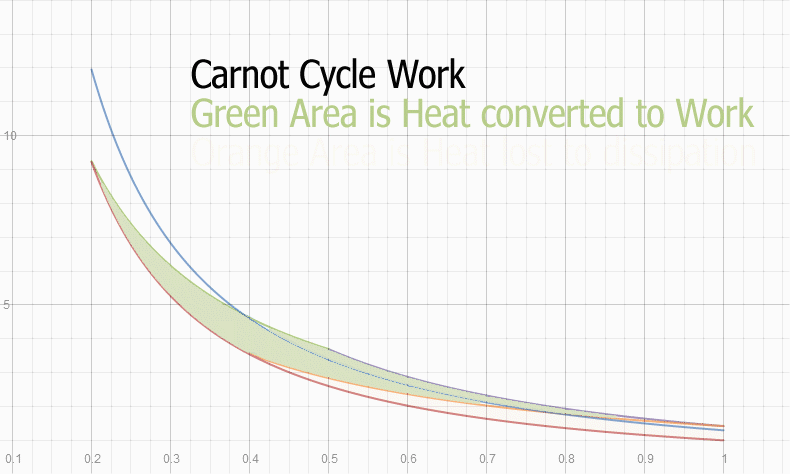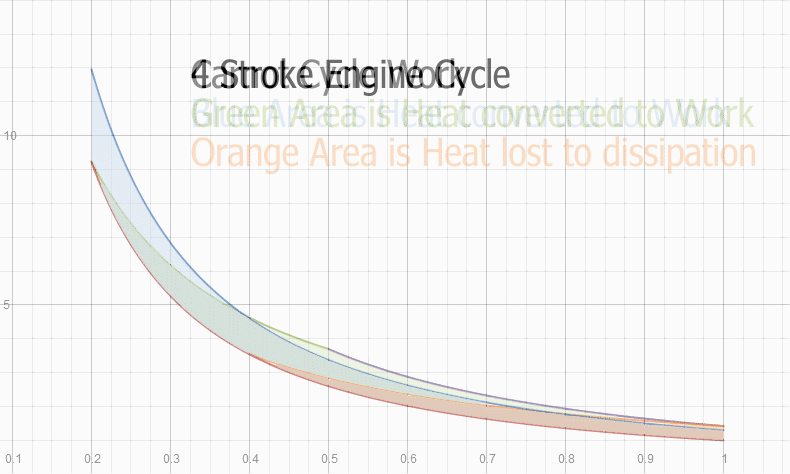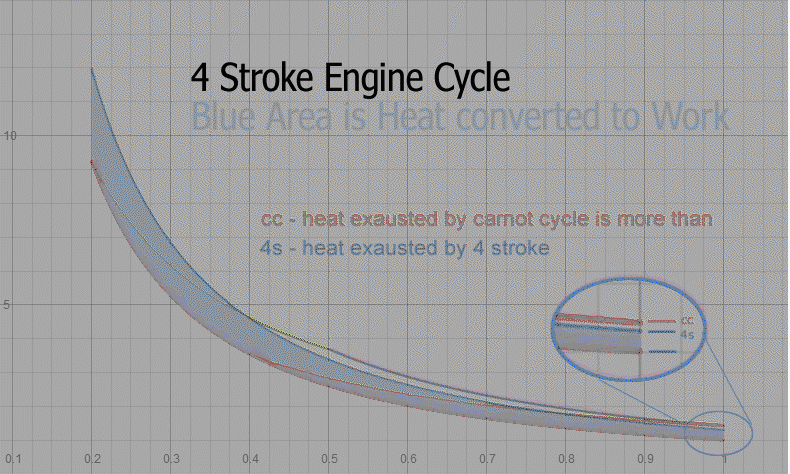
The amount of heat converted to work, is a constant for each vapor and each volume expansion ratio.
If all the heat is put in before any volume expansion, the full range of expansion operates on all the heat energy.
If part of the heat is added after some expansion is done, that heat will have a smaller expansion ratio than heat put in at the beginning.
Example: Consider a 1 to 10 expansion ratio piston. The Carnot cycle will add heat until about half way through the expansion. The heat present at the beginning of expansion, experiences 1 to 10 expansion, so its Work Ratio is about 58%. Heat put in at the middle of the expansion, experiences only a 1 to 2 expansion from that point, so it's Work ratio is about 23%.
|
Carnot Cycle overlayed with 4 stroke engine cycle
|

